Cast Resin Transformer
CAST RESIN TRANSFORMERS
Thanks to the long experience of SHERPA and to the sophisticated calculation and design techniques used, our transformers for distribution, rectification and traction can be provided in a very large range of sizes, primary and secondary tensions, insulation classes and losses.
Following tables present the technical features of some transformers in our production range. They were chosen according to norm requests and to market preferences in power distribution sector for the main industrial countries. Different powers, as well as different primary and secondary tensions, are nonetheless part of our production range and application experience. In this case it is useful to get in contact with us for technical data confirmation.
Technical characteristics of SHERPA transformers
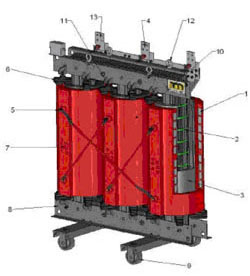
1. HV windings in coils of aluminium band, cast in resin under vacuum.
2. Core composed of three columns made in grain oriented magnetic steel sheets, also available with much reduced losses.
3. LV windings of aluminium foil and insulation material, impregnated under vacuum.
4. LV connections at the top (standard production), or at the bottom (on request).
5. HV connections also available with Elastimold elbow connectors.
6. Spacers with rubber inserts reduce vibration transmission between core and windings, hence reducing transformer working noise.
7. Off load tap changing links on the HV winding allow step by step regulation to suit supply voltage.
8. Main structure and trolley frame manufactured of robust painted steel.
9. Rollers adaptable in two perpendicular directions.
10. The epoxy resin insulation has a high inflammability point and high self extinguishing characteristics, making the transformer maintenance-free.
11. The operating temperature is controlled with Pt100 or PTC probes, placed in each of the LV windings.
12. Lifting lugs for safe lifting on 4 points.
13. On request LV connection ready for Zucchini busbars.
14. The frame is ready to install an integral steel enclosure.
15. Insulating materials for class F products, winding over temperature of 100° K.
SHERPA designs and manufactures CRTs for:
Distribution of electrical energy
• Hospitals
• Shopping Centre’s
• Airports
• Industrial applications in general
• Steel mills
Conversion and rectification 6/12/24 pulses
• Air conditioning systems (HVAC)
• UPS and no-break power system
• Railways, underground railways and tramlines
• Lifting and pumping plants
• Industrial plants with AC / DC converters.
• Welding lines
• Induction furnaces
Step up transformers
• Wind generation parks
• Cogeneration plants
DEFINITION
DEFINITION
RATINGS
A dry-type transformer is one in which the magnetic circuit and the windings are not immersed in an insulating liquid, IEC 726.
SCOPE
This catalogue refers to cast-resin transformers with rated power levels between 100 and 2500 kVA, with higher voltage for the material, up to and including 36 kV. In addition, Electrical Power Systems manufactures transformers up to 5000 kVA in the 36 kV series.
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
The general details of our transformers are the follows: three-phase, continuous operation, indoor installation, degree of protection IP00, frequency 50 Hz, AN cooling, thermal Class F.
MANUFACTURING STANDARDS
The transformers described in this catalogue are designed and tested in accordance to the European Union Harmonisations Documents HD 538 and HD 464 as well as IEC 726, IEC 76 standards. However, and by request, they can be manufactured according to other national or international standards.
RATINGS
A dry-type transformer is one in which the magnetic circuit and the windings are not immersed in an insulating liquid, IEC 726.
160 – 250 – 315 – 400 – 500 – 630 – 800 – 1000 – 1250 – 1600 – 2000 – 2500 – 3150 kVA
HIGH VOLTAGE
This material is designed for voltages of ≤ 36. Specific figures are not given for this parameter because of the wide variety of voltages used. Transformers can be supplied on demand to run at two different primary voltages.
LOW VOLTAGE
The no load voltage is allocated at 400 V, though other voltages can be supplied on demand.
When usage requires two voltages, transformers with two simultaneous voltages can be supplied.
In this case no-load voltages are set to 400 and 231 V.
VECTOR GROUP
The connections normally used are as follows:
• For rated power levels of 160 kVA or less: Yzn11 or Dyn11
• For rated power levels 160 kVA: Dyn11.
TEMPERATURE RISE
The connections normally used are as follows:
• For rated power levels of 160 kVA or less: Yzn11 or Dyn11
• For rated power levels 160 kVA: Dyn11.
INSULATION LEVELS
As per IEC 76, BS 171 and VDE 532 standards these are set in accordance with the highest voltage for the material, being the level immediately above the rated voltage.
SNO-Energietechnik transformers are in the F insulation class, which, according to IEC 726, have a temperature rise of 100 K.
ADVANTAGES OF CAST RESIN TRANSFORMERS
Cast resin transformers have the following advantages:
• Self-extinguishing
• In case of fire outside the transformer but which affects it, it burns only with difficulty and with poor flame, which rapidly dies out when the source of fire ceases.
• High Thermal inertia
• Due to a greater mass than equivalent transformers in liquid, the time constant is much greater, so that there is a better tolerance of overloads of short duration.
• Compactness
• The only components being the magnetic circuit, the windings and the fixing elements, the design is very compact, thus it is a robust assembly and vibration-proof. This makes transformers ideal for installation in mobile material.
• Good resistances to short-circuits
• As a result of the cast resin which surrounds the conductors as well as linking them strongly together, resistance to the electrodynamics forces generated in a short-circuit is very high. Again, as the density of current is lower than that the transformers with liquid, the maximum transient temperature reached in a short circuit is much lower than the limits specified in IEC 76.
• Reduced maintenance
• All that required is to clean dust off the surfaces, should it occur
• Easy Installation
• Protection against contacts is sufficient, since there is no need for a deposit to hold the liquid, nor brickwork installation
CONSTRUCTION DETAILS
I- MAGNETIC CIRCUIT
This is made in oriented grain cold rolled magnetic sheet with low losses, covered on both sides with a fine coat of inorganic insulation material. The cross-section is identical for legs and yokes with a step-ped shape. The number of steps used is according to the rated power.
The 45°C type of joints used for the union between legs and yokes and the absence of bolts going through the yokes gives resulting low no load losses.
Both the legs and yokes are bound with special insulating heat-shrink tape, which makes for compact assembly and low vibration, reducing the noise level. As a finish, a thick coat of compactant resin is applied to the entire exterior surface of the magnetic circuit, ensuring a permanent low noise level and preventing rust.
III- HIGH VOLTAGE WINDING
This is made in oriented grain cold rolled magnetic sheet with low losses, covered on both sides with a fine coat of inorganic insulation material. The cross-section is identical for legs and yokes with a step-ped shape. The number of steps used is according to the rated power.
The 45°C type of joints used for the union between legs and yokes and the absence of bolts going through the yokes gives resulting low no load losses. Both the legs and yokes are bound with special insulating heat-shrink tape, which makes for compact assembly and low vibration, reducing the noise level.
As a finish, a thick coat of compactant resin is applied to the entire exterior surface of the magnetic circuit, ensuring a permanent low noise level and preventing rust.
II- LOW VOLTAGE WINDING
Normally this winding is made with a bare-strip form conductor, although with low power levels a rectangular wire insulated with NOMEX is also used. In both cases insulating material pre impregnated with epoxy resin is used between the layers which, in polymerizing, unites the conductors among themselves, producing a compact assembly with high resistance to the stress developed during a short-circuit.
This type of windings allows the insertion of one or more axial ducts, which facilitates the rapid dissipation of beat and the absence of hot points. Finally, the finished coil is impregnated with epoxy resin which, once polymerized, gives it strong resistance against damp.
V- STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS
This winding is carried out with two different types of conductors: bare strip or enamelled wire. Strip windings are formed by several coils or disks made one after another in a continuous process. The turns, their insulations, the taps and the different positions are fully programmed, controlled, and directed through a computer integrated into the automatic winding machine itself. Enamelled wire conductor windings are also made in “wafers” each one formed of several layers, between which insulating material is interleaved.
IV- CASTING PROCESS
The resin used by SNO-Energietechnik is of epoxy type with thermal class „F“, for a temperature rise of 100 K (maximum temperature of insulating system 155°C) The casting system prepared for our manufacturing installation contemplates the use of four principal components:
• Epoxy resin
• Filler material
• Hardener
• Coloring
The casting process, the dosage of components and the different steps from moulding to polymerization. The mixture of resin and hardener, with the filler material, is degassed under vacuum and at controlled temperature, before a final mixing and introduction into the moulds under vacuum. The high technology of our casting station and the quality of the components used enables us t manufactures cast coils with practically total absence of partial discharges.
The structural fixing elements, both the tightening beams and the support and transport frames, are made of steel sections. In order to eliminate vibration, layers of resilient material are interleaved between the magnetic circuit and the structural elements and also between the windings and supporting parts. This means that the expansion of the coils produced by increases of temperature is absorbed, as well as the vibration of the magnetic sheet due to construction.
VI- CONNECTIONS
The High Voltage connection terminals are located at the front of the transformer and those for
Low Voltage are the top.
The High Voltage terminals are of tinned copper with a hole of 14 mm diameter.
The Low Voltage terminals are always flag-type terminals with two or more holes 14 mm.
HIGHEST VOLTAGE FOR MATERIAL 12kV
Rated Power 160 – 3150 kVA
Rated Voltage HV 10 kV
Primary voltage tappings 2 x +/-2, 5%
Rated voltage LV 0, 4 kV no load
Frequency 50 Hz
Insulation level HV/LV LI 60-AC28/- AC3 [kV]
Thermic class F/F (HV/LV)
Degree of protection IP00 (Indoor)
Winding material HV: AL, LV: AL
Type of cooling AN
Installation < 1000 m a.s.l.
Ambient temperature 40°C
BASIC EQIUPMENT
Includes in all transformers supplied:
• Rating plate
• 4 lifting lugs
• 4 towing holes
4 two-way, 90°directional wheels
OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES
• Monitoring equipment with temperature indication and alarm and tripping contacts
• Forced cooling equipment
• Plug-in connections
• Device for tapping changeover
• Metal casing, protection IP31
VENTILATION
In order to avoid excessive and damaging heating, and for correct operation, it is essential to dissipate the thermal energy produced by the transformer during operation.
The natural circulation of air is directed from the lower part to the upper (chimney effect) and the dimensions of the openings are according to the losses to be dissipated and the temperature of the air entering and leaving the cell. The lower opening must be located close to the transformer, as low as possible, while the upper one must have a cross-section 15% greater to compensate for the lesser density of the hot air.
Equipment for quality assurance type tests:
Lightning impulse test
Partial discharge measurement
Noise level measurement
Heat run test
Zero phase sequence impedance
capacity
Environment Tests
No condensation on the transformer, negligible pollution. Installation in dry and clean ambient.
HV coil of a 1600 kVA transformer, after a Class F1 fire resistance test.
Occasional condensation and little pollution.
The transformer is subject to severe condensation or to heavy pollution or to a combination of both.
Climatic Tests
The transformer is unsuitable for operation at temperatures below - 5°C but may be exposed to –25°C during transportation and storage.
The transformer is suitable for operation, transport and storage down to –25°C.
Fire Behavior Test
No fire hazard is envisaged and no measures to limit the flammability are taken.
The transformer is subject to fire hazard and a restricted flammability is required. Self-extinction of fire shall take place within a specified time period.
Accessories on Request
• Steel enclosures, fixed to the transformer
Protection degree IP21 - IP31 - IP23
Insulation class 12 - 17, 5 - 24 kV
• Steel enclosures, fixed to the floor
Protection degree IP21 - IP31 - IP23
Insulation class 12 - 17, 5 - 24 kV
On specific customers request Version for external installation available.
• Ventilation fans
For temporary rating increase +30% or +40%
Complete with fans control units
• Temperature monitoring units
For Pt100 probes
For PTC probes
• HV elbow connectors, Elastimold type
• Ant vibration devices
For extra reduction noise level
Installation under the rollers
Installation on the floor
• Surge arrestors
For a complete protection of the transformer.
• Bars shift on request


 +88-01611-743772, 01922-119600
+88-01611-743772, 01922-119600